Our engineering teams have been hard at work improving the overall experience for our customers. We continue to focus on ways to make Vendia more secure, more performant, and more transparent. With recent launches we have made strides in each of these areas. While these are not all the things we've been working on, we think these are the ones you will be most excited to try out.
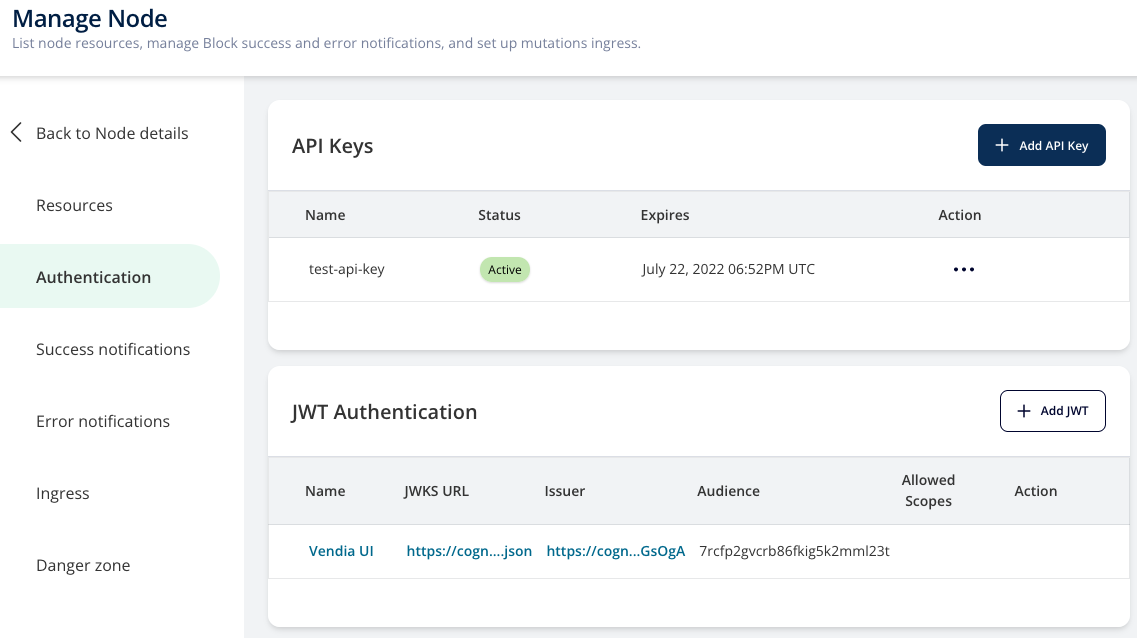
New API Keys and JWT authentication
Security is our top priority at Vendia. We are always looking for ways to make using and interfacing with Vendia more secure. We recently overhauled our APIs with new, more secure API keys and new methods for securely authenticating users using JSON Web Tokens (JWT).
API Keys
API keys enable programmatic server-to-server access to the Node. Now you can easily add new API keys or rotate existing ones. Additionally, you can set an expiration date on API keys after which time they will no longer work.
Note: All Unis and Nodes using API keys have been migrated to the new API key format. The new API Keys are passed to Vendia via the Authorization header of each GraphQL request. Previously, Vendia supported use of the x-api-key header for passing API keys. We have removed the capability to use the x-api-key and all API requests must use the Authorization header.
JWT authentication
JSON Web Tokens (JWT) are an open, industry standard RFC 7519 method for representing claims securely between two parties. Enabling JWT Authentication for your Vendia Node allows for both client-to-server and server-to-server access. With this authentication method, you specify your external identity provider's public key details so that the Node can validate the incoming token. Our implementation of JWT authentication supports many different identity providers (IdPs), such as Okta, Auth0, AWS Cognito, and Azure Active Directory.
You can manage API Keys and JWT authentication via the Vendia console, through the CLI, or using the GraphQL APIs for your Node.
Low Latency Operations
Vendia had chosen a default read-after-write consistency mode such that transactions would need to be written to the world state and the ledger on a node before you could query the data. We chose this design to prevent potential dirty reads.
But, there may be cases where you prefer response speed over data completeness (i.e., potentially a dirty read). For example, an application that shows the approximate availability of inventory might prefer to show inventory data quickly—even if that data is from a few minutes ago, rather than waiting for the most up to date inventory count. Likewise, there may be use cases where you prefer data completeness over response speed (i.e., there can be no dirty reads). For example, you may have the need to only return data when all participants (nodes) have accepted and written the transaction into the world state and the ledger.
To address the different needs of customers, we launched different consistency modes for reading (querying or listing), subscribing, or performing synchronous mutations. Clients have the option of providing their preferred consistency mode when issuing a query, subscription or a synchronous mutation.
Query Consistency Modes
| Type of Consistency | Dirty Reads | Operation Latency | Consistency Guarantees |
| CACHED | Likely | Fastest | Transactions are written to a local cache on a given Node and can be out of date up to cache timeout. |
| NODE_COMMITTED | Possible | Fast | Transactions are written to the world state on a given Node but, perhaps, not yet to the ledger. |
| NODE_LEDGERED | No | Slow | Transactions are written to the world state and ledger on a given Node. |
| UNI_LEDGERED | No | Slowest | Transactions are written to the world state and ledger on all Nodes. |
Query Example
query getShapeQuery {
get_Shape(id: "0180f1d5-7b0c-c03a-dd22-54eb75b807ef", readMode: CACHED) {
color
name
num_sides
}
}
Synchronous Mutation Consistency Modes
| Type of Consistency | Dirty Reads | Operation Latency | Consistency Guarantees |
| NODE_COMMITTED | Possible | Fast | Transactions are written to the world state on a given Node but, perhaps, not yet to the ledger. Writes are guaranteed to be read on the local node if using NODE_COMMITTED read mode. |
| NODE_LEDGERED | No | Slow | Transactions are written to the world state and ledger on a given Node. |
| UNI_LEDGERED | No | Slowest | Transactions are written to the world state and ledger on all Nodes. |
| ASYNC | N/A | Fastest | Transactions are queued up and a transaction ID is returned that can be polled. Transactions can be queried once they are written to the world state and the ledger on a given Node. |
Synchronous Mutation Example
mutation addShapeMutation {
add_Shape(
input: {color: "blue", name: "hexagon", num_sides: 6}
syncMode: UNI_LEDGERED
) {
result {
_id
}
}
}
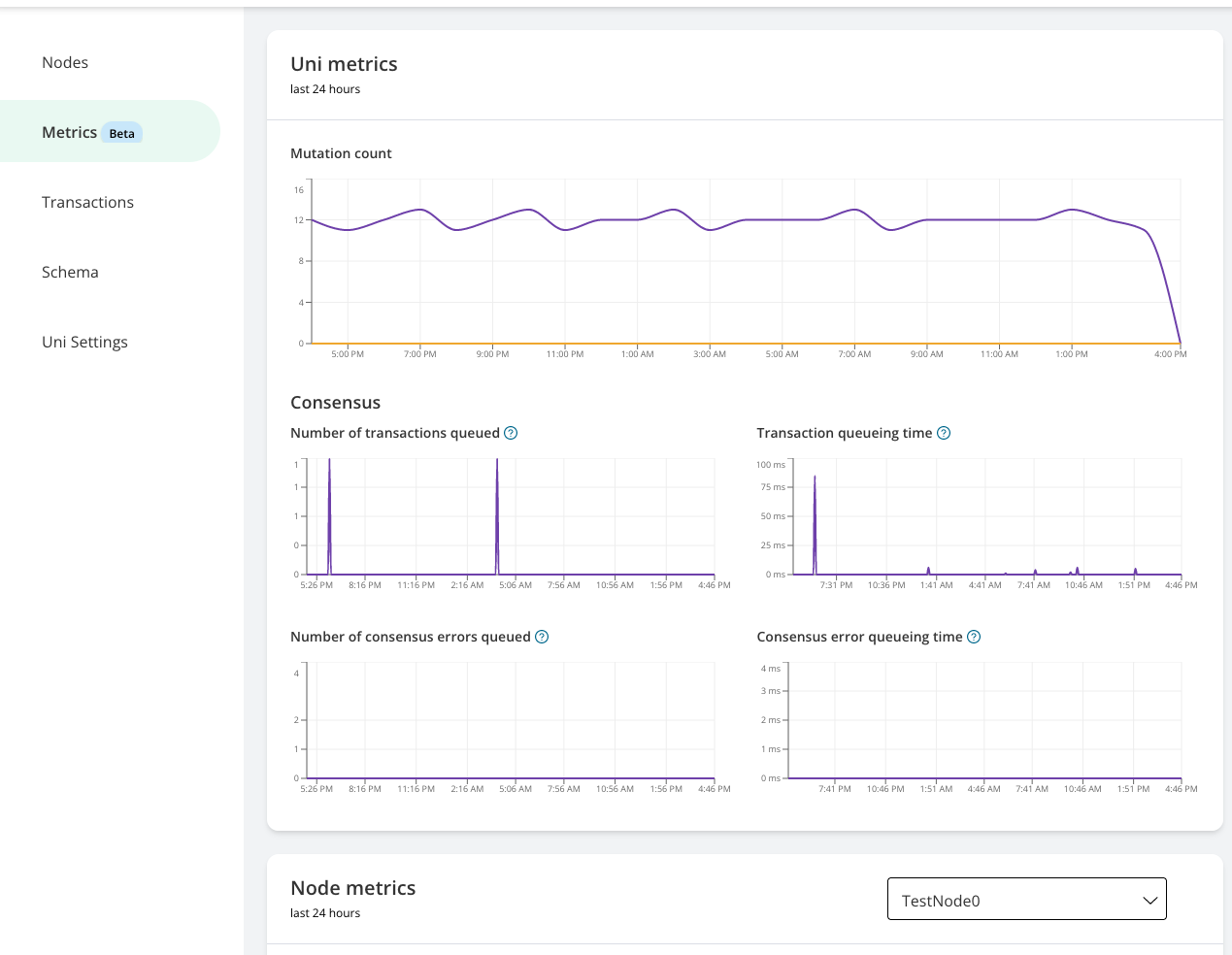
Vendia Metrics
Most companies will go through an operational readiness review (ORR) before launching a product or a new feature. ORRs all have the same goal: To help you find blind spots in your operations ahead of launch. One of the main goals of an ORR is to ensure you have the right metrics and alarms to ensure the availability of the product or feature.
Vendia Metrics are a set of operational metrics for Nodes and Unis to give you insight into how you Unis and Nodes are performing. Vendia metrics are enabled for all Nodes and Unis in your account without any additional configuration. The following metrics are now available:
- Mutation Count
- Number of transactions queued
- Transaction queuing time
- Number of consensus errors queued
- Consensus error queueing time
- GraphQL API request count
- GraphQL API latency
- GraphQL API error rate
- End-to-end mutation latency
All Vendia Metrics are visible over a 24-hour period. To view the Vendia Metrics, navigate to a Uni in the Share console and click on the “Metrics” button along the left hand column.